Immunosuppression of the tumor microenvironment is the main obstacle to tumor immunotherapy. Interferon stimulating factor (STING) agonists can trigger inflammatory innate immune responses, potentially overcoming tumor immune suppression. Although STING agonists may have the potential to become cancer treatment drugs, tumor resistance to STING monotherapy has emerged in clinical trials, and its mechanism is still unclear.

On September 4, 2023, Professor Ren Xiubao's team from the Cancer Hospital of Tianjin Medical University published an article titled "Blocking Tim-3 enhances the anti tumor immunity of STING antigen ADU-S100 by clearing CD4+T cells through regulating type 2 conventional dendritic cells" in Theranos (IF=12.4).
This experiment used a mouse tumor model to measure the in vivo anti-tumor immune effects of STING agonist ADU-S100 (S100) and anti-T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3 antibody (α Tim-3). The activation of tumor specific T cells and changes in the tumor microenvironment were detected using flow cytometry. Simultaneously, the maturation and function of dendritic cells (DCs) were measured, as well as the importance of CD4+T cells in combination therapy. In addition, the effect of S100 on CD4+T cells was validated through in vitro experiments. Finally, the impact of conventional dendritic cells (cDCs) with high expression of Tim-3 in human tumor samples on survival or therapeutic efficacy was further evaluated.
S100 enhanced the response of CD8+T cells by activating cDC1, but failed to activate cDC2. Mechanistically, the administration of S100 resulted in upregulation of Tim-3 in mouse and human cDC2 (Tim-3+cDC2), which has immunosuppressive effects. Tim-3+cDC2 inhibited CD4+T cells and weakened the anti-tumor response driven by CD4+T cells. The combination therapy of S100 and α Tim-3 effectively promoted the maturation and antigen presentation of cDC2, released CD4+T cells, thereby reducing tumor burden and prolonging survival. In addition, a high percentage of Tim-3+cDC2 in the human tumor microenvironment indicates poor prognosis, and the abundance of Tim-3+cDC2 may serve as a biomarker for CD4+T cell quality and a contributing indicator for immune therapy responsiveness.
This study demonstrates that blocking Tim-3 can enhance the anti-tumor immune effect of STING agonist ADU-S100 by regulating cDC2, releasing CD4+T cells. It also reveals the inherent barriers of ADU-S100 monotherapy and provides a combined strategy to overcome tumor immune suppression.
Experimental part
This experiment collected tumor samples from 58 lung cancer patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) or neoadjuvant pembrolizumab combined with chemotherapy (NAPC). Obtain images using the TissueFAXS Spectra panoramic multispectral tissue scanning quantitative analysis system from TissueGenomics. Obtain images and use StrataQuest software for quantitative analysis to evaluate the relationship between tumor infiltrating TIM-3+CC2 or CD4+T cells and therapeutic efficacy.
Panel : CD11c、CD1C、Tim-3、CD4、Foxp3 and DAPI
In order to verify the negative regulatory effect of Tim-3 expressed on CD4+T cells on DCs, the authors of the article analyzed the relationship between Tim-3+cDC2 and CD4+T, and evaluated the relationship by referring to the main pathological response (MPR) as a clinical characteristic indicator.
Considering that CD4+T cells are downstream of cDC2 in immune function, their interactions can only be roughly evaluated at the global level in the traditional sense, but cannot be accurately quantified. Therefore, the authors of this article used Tissue Cytometry technology to conduct spatial quantitative analysis of the distribution of Tim-3-cDC2/Tim-3+cDC2 and CD4+T/Treg cells. Researchers compared the distribution density of CD4+T cells within a radius (r=30 μ m) of Tim-3-cDC2/Tim-3+cDC2 using the Poisson distribution principle according to literature records. They found that in NAC and NAPC patients, the CD4+T cells around Tim-3+cDC2 were significantly reduced compared to Tim-3-cDC2, indicating a reduced possibility of cell contact between CD4+T and Tim-3+cDC2. This analysis provides preliminary evidence for the relationship between poor prognosis in Tim-3+cDC2 tumor patients, which urgently needs to be confirmed by relevant clinical trials, "the author wrote in the article.
Most existing technologies use spatial coordinate methods to study cellular spatial biological information. However, when cells are spindle shaped or irregular in shape, the center point of the cell cannot represent their true tissue morphology contour, resulting in biased analysis results. Tissue Cytometry technology is different from other techniques in that it uses in situ real cell morphology and contours, and uses the distance calculation of real pixels in the original imaging results as the basis for distance analysis. This not only obtains the distance relationship of real cells, but also calculates their microenvironment distribution level through tissue cell morphology, making the analysis results more accurate and reliable.
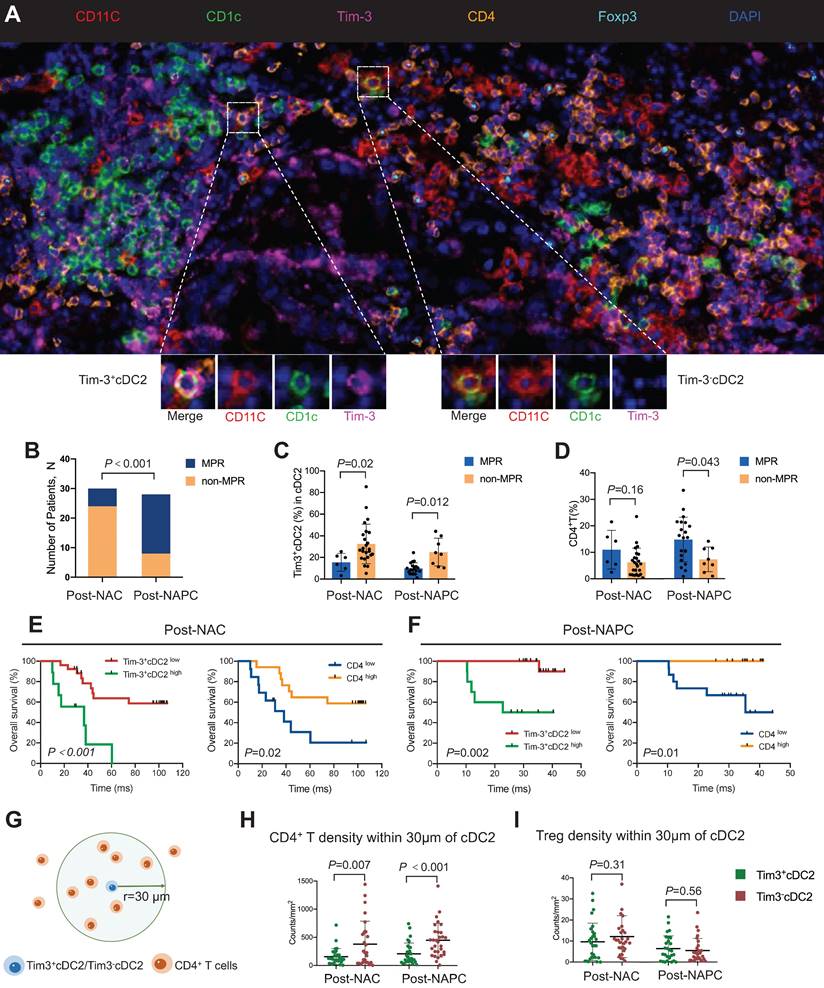
Figure 1 High proportion of TIM-3+cDC2 predicts poor prognosis in cancer patients
(A)Multiple immunofluorescence images of lung cancer samples after treatment
(B)Comparison of MPR percentages among patients receiving NAC or NAPC treatment. Comparison of (C) Tim-3+cDC2 or (D) CD4+T cells in MPR or non MPR patients receiving NAC or NAPC treatment.
(G-I) Using spatial analysis methods, calculate the density of cells of interest within a radius of 30 μ m around the reference cell and plot it. Compared with Tim-3+cDC2 cells in NAC and NAPC patients, the density of (H) CD4+T cells and (I) Treg cells within a 30 μ m range around Tim-3-cDC2 cells is as follows.