Axillary lymph nodes (LNs) are the main metastatic sites of breast cancer (BC). However, the interaction between tumor cells and immune cells in metastatic lymph nodes (mLNs) remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the effect of CD24hiCD27+regulatory B cells (Bregs) in mLNs on the drug resistance of BC cells.
On October 11, 2023, the Department of Breast Surgery at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine published a research paper titled CD24hiCD27+Brgs within Metastatic Lymph Nodes Promoting Multi Drug Resistance in Breast Cancer in the Journal of Clinical Cancer Research. The study revealed the key role of CD24hiCD27+Brgs in promoting drug resistance by interacting with BC cells within mLNs, providing new evidence for the use of chemotherapy immunotherapy combination strategies in BC patients.
We collected mLN samples from BC patients receiving standard neoadjuvant therapy (NAT) and analyzed the spatial distribution characteristics of CD24hiCD27+Brgs through multi-color immunofluorescence staining. The effect of CD24hiCD27+Bregs on the drug resistance of BC cells was evaluated through in vitro experiments. The strategy of blocking the interaction between Bregs and BC to improve tumor regression within mLNs was evaluated using a mouse model with mLNs.
There is a close spatial correlation between activated CD24hiCD27+Brgs and residual tumor cells in mLN in BC patients receiving NAT.
Mechanistically, CD24hiCD27+Bregs significantly enhance the multidrug resistance and stem like characteristics of BC cells by secreting IL-6 and TNF-a. More importantly, BC cells further promote the activation of CD24hiCD27+Brgs through CD40L - and PD-L1-dependent proximal signaling, forming a positive feedback pattern. PD-L1 blockade significantly weakened the drug resistance of BC cells induced by CD24hiCD27+Bregs, and the addition of anti-PD-L1 antibodies during chemotherapy can improve tumor cell regression in mLNs.
实验部分
This article uses the TissueFAXS Spectra panoramic multispectral tissue scanning quantitative analysis system from TissueGenomics to collect multi-color immunofluorescence images of tissue sections from BC tumors and control LN from 7 different patients.
Panel 1 : pan-CK,CD19,IL-10,DAPI
Panel 2: pan-CK,CD19, CD24, CD27,IL-10,DAPI
Panel 3 :pan-CK, CD19, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10, DAPI
In order to study the reliability of the data, the author of this article first conducted precise quantitative analysis of the single-cell expression level of IL-10 secreted by B cells using Tissue Cytometry technology, clarifying that the residual tumor cells of standard NAT that survived in mLN were closely related. To achieve this goal, immunofluorescence staining was performed using Panel1:Panel 1 : pan-CK,CD19,IL-10,DAPI。
Next, in order to explore the activation status of immune cells, the researchers took CD24hiCD27+Bregs in breast cancer mLN as the research goal, not only quantified its single cell expression level, but also analyzed its spatial role relationship in the distribution of tumor microenvironment. Research has found that when lymphoid follicles rich in B cells are disrupted, B cells are more distributed around metastatic tumor nests. In this section, we also utilized Tissue Cytometry technology and Panel2:Panel 2: pan-CK,CD19, CD24, CD27,IL-10,DAPI
In the next step, based on the study of B cells expressing IL-10, researchers combined cell subtypes expressing IL-6 and/or TNF-a to investigate their relationship with residual tumor burden. The results showed a positive correlation, thus proving that the effect of CD24hiCD27+Breg derived cytokines, namely TNF - and IL-6, rather than IL-10, is the cause of BC cell stemness and multidrug resistance. In this part of the study, Tissue Cytometry technology was used for analysis, using Panel combination 3:pan-CK, CD19, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10, DAPI
Although this article extensively utilized flow cytometry and transcriptome techniques for quantitative analysis of cell phenotype and expression levels, a validation standard using Tissue Cytometry as an in situ validation method was established for key data. Compared to traditional research methods, the data obtained in this way is not only more comprehensive, but also studies the spatial distribution relationship from the perspective of single-cell protein expression, which is the most reflective research level of the real situation of organisms.
In terms of spatial distance analysis, considering the distribution characteristics of cells in the tumor microenvironment, the closer the distance to the tumor boundary, the more significant the relative effect. Therefore, the author of the article adopted three ranges of distance gradient 0-25 μ m, 25-50 μ m, and 50-100 μ m after considering the analysis of the relationship between microenvironment effects. This not only refined the accuracy of tumor microenvironment research, but also took into account the data analysis of distant cells.
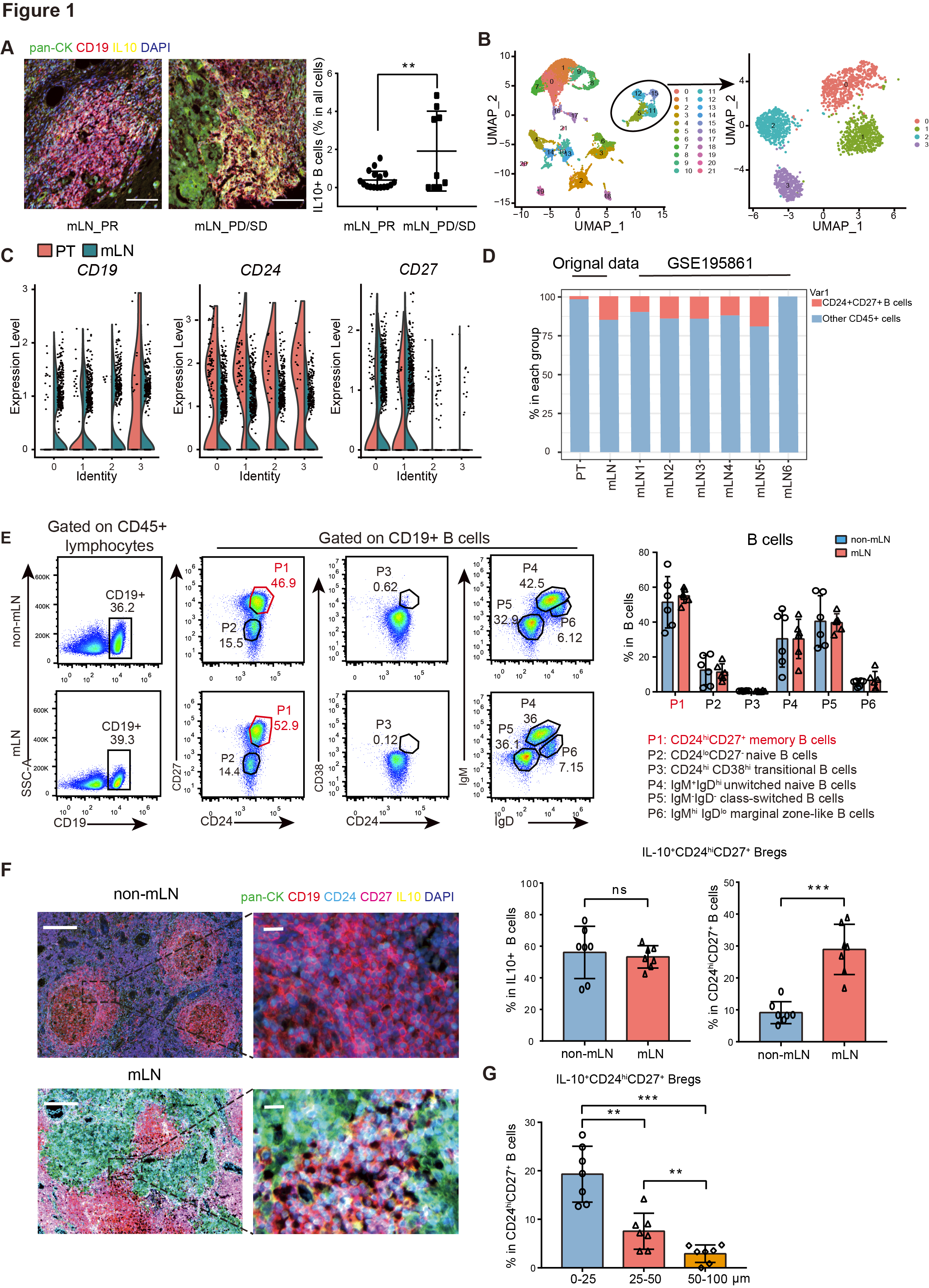
Figure 1 CD24hiCD27+Brgs are the most predominant B cell subpopulation in LNS, located very close to tumor cells in MLN.
A: Multicolor immunofluorescence images of IL-10 (yellow), CD19 (red), pan CK (green), and DAPI (purple) in patients with partial response (PR, n=17) and progressing metastatic lymph nodes (MLN). Quantify the proportion of IL-10+CD19+cells in mLN with different drug responses based on multi-color immunofluorescence image analysis of IL-10 and CD19 expression.
F: Multi color immunofluorescence images stained with IL-10 (yellow), CD19 (red), CD24 (sky blue), CD27 (purple red), pan CK (green), and DAPI (purple) in non MLN and MLN of BC patients. Quantitative analysis of the percentage of IL-10+CD24hiCD27+B cells in IL-10+B cells.
G: The proportion of IL-10+CD24hiCD27+B cells surrounding pan CK+in peripheral blood of BC patients.
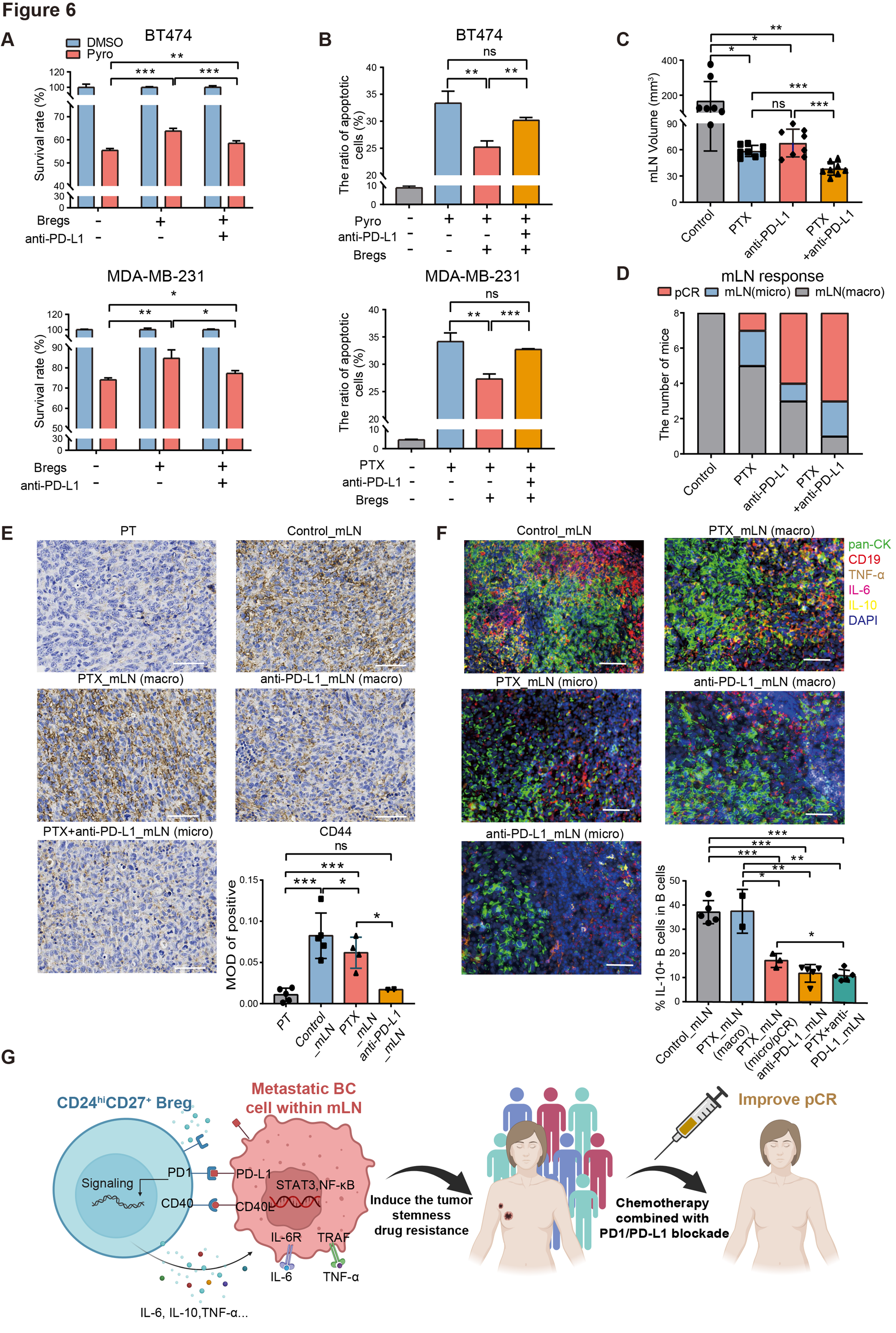
Figure 2 F: Different treatment groups of mice bone marrow mononuclear cells pan CK CD19、IL-10、 Multi color immunofluorescence images of tumor necrosis factor - α and IL-6. Statistical analysis of the percentage of IL-10+B cells to B cells in bone marrow mononuclear cells of mice in different treatment groups.