Worldwide, breast cancer is the main type of cancer for women, accounting for 25% of all cases. It is more common in developed countries. The incidence rate of women is more than 100 times that of men. The five-year survival rate in Britain and the United States is between 80% and 90%. In developing countries, the five-year survival rate is relatively low. In 2018, it resulted in 20000 new cases and 627000 deaths.
The outcome of breast cancer varies according to the type of cancer, the degree of disease, and the age of the patient. The clinical and molecular heterogeneity of the tumor has a variety of internal subtypes, and each subtype has different molecular characteristics, treatment responses, and prognosis. Although the development of more and more immunotherapy methods shows the potential of immunomodulation therapy for breast cancer, how to transform basic tumor research into clinical practice is still a topic worthy of discussion for a long time.
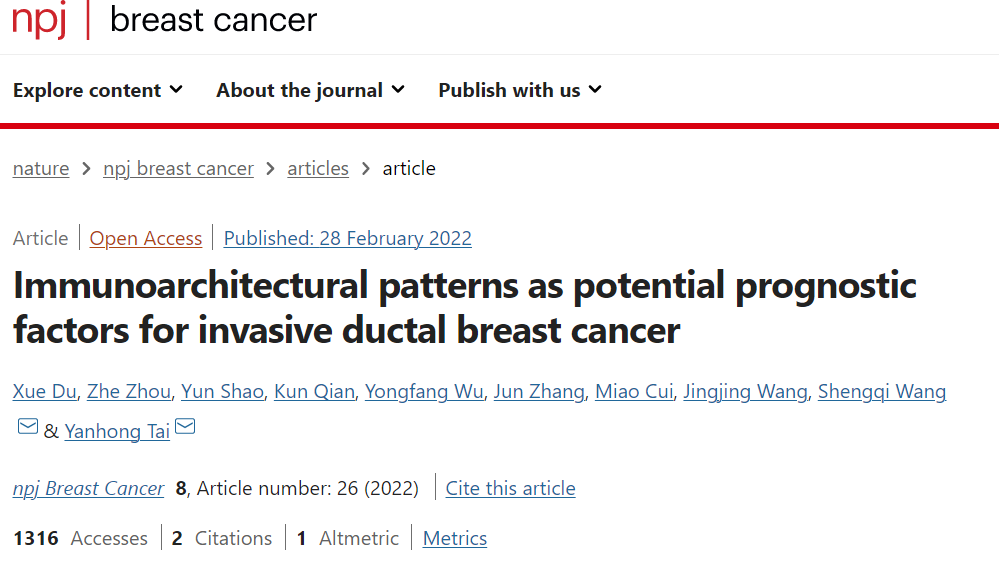
The main content of this study is about the immune structure model as a potential prognostic factor for invasive ductal breast cancer. At present, tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in invasive breast cancer are only evaluated according to their number, and their spatial distribution is rarely studied. The density and spatial localization of TILs are correlated with molecular subtype based clinical pathological features and PD-L1 expression.
Professor Tai Yanhong from the Fifth Medical Center of the General Hospital of the Chinese People's Liberation Army, By exploring the hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining sections of 579 tissue samples from patients with no special type of invasive breast cancer (IBC-NST), to determine the tumor immune structural patterns (IP) and TIL density, involving the determination of comprehensive data such as lymph cell density, location, immunophenotype and combined histopathological characteristics (such as histological grading, clinical staging, molecular type and survival status) of IBC-NST patients, and combining with sequencing technology, this paper introduced a very expansive research perspective from the multi group level.
All staining images and in situ spatial quantitative analysis results presented in the article are from the Tissue Cytometry technology of TissueGenomics company.
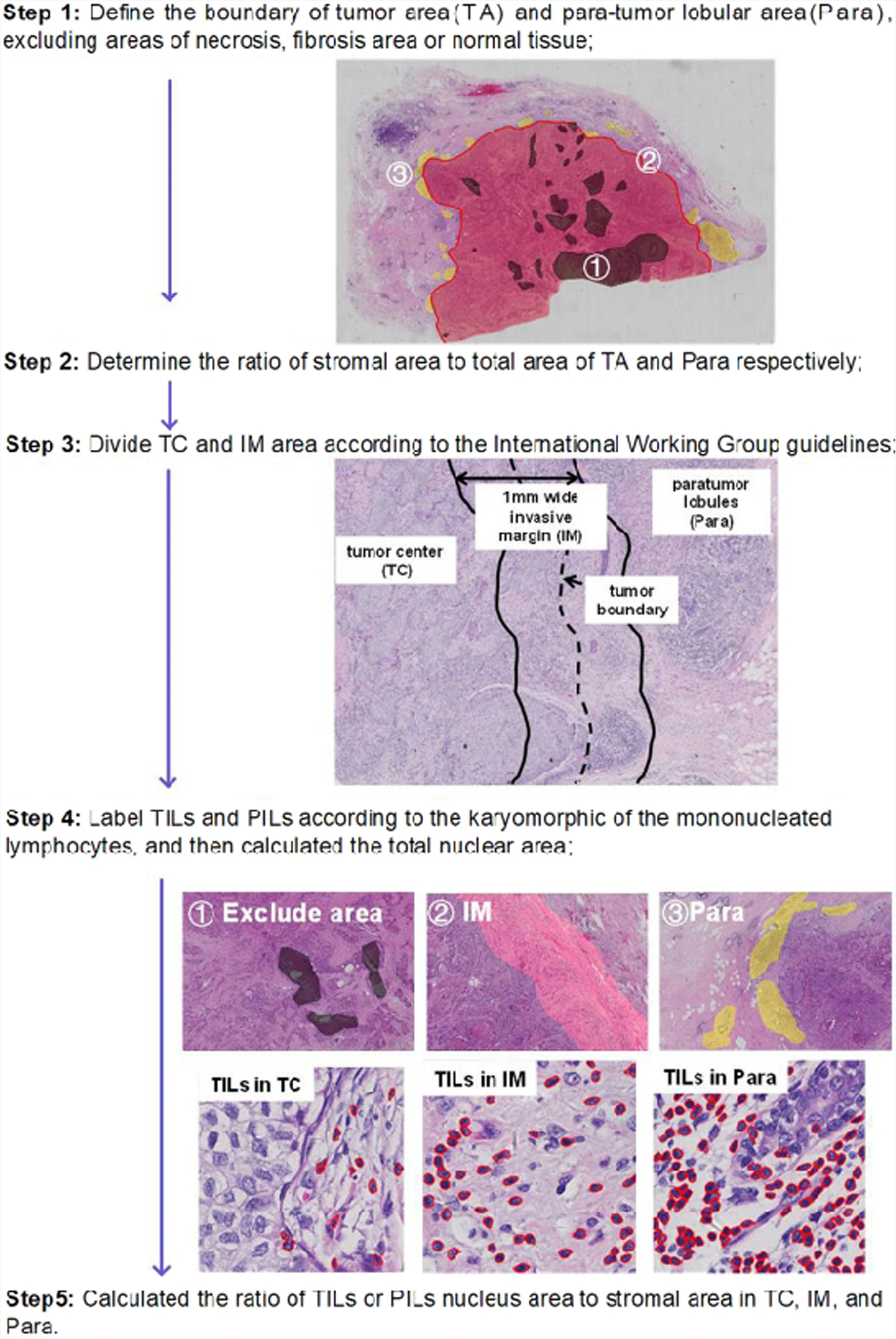
Figure 1 Program description for analyzing TIL and PIL in IBC-NST samples
TILs tumor infiltrating lymphocytes, PILs paraneoplastic infiltrating lymphocytes, IBC-NST infiltrating breast cancer has no special type.
The author of this article evaluated the tumor immunity of 579 cases of primary IBC-NST and divided them into five IPs, as shown in the figure. Among them, IP2 (19/579, 3.28%) had the lowest number of cases, followed by IP1 (69/579, 11.92%), IP3 (110/579, 19.00%), IP4 (130/579, 22.45%), and IP5 (251/579, 43.35%)
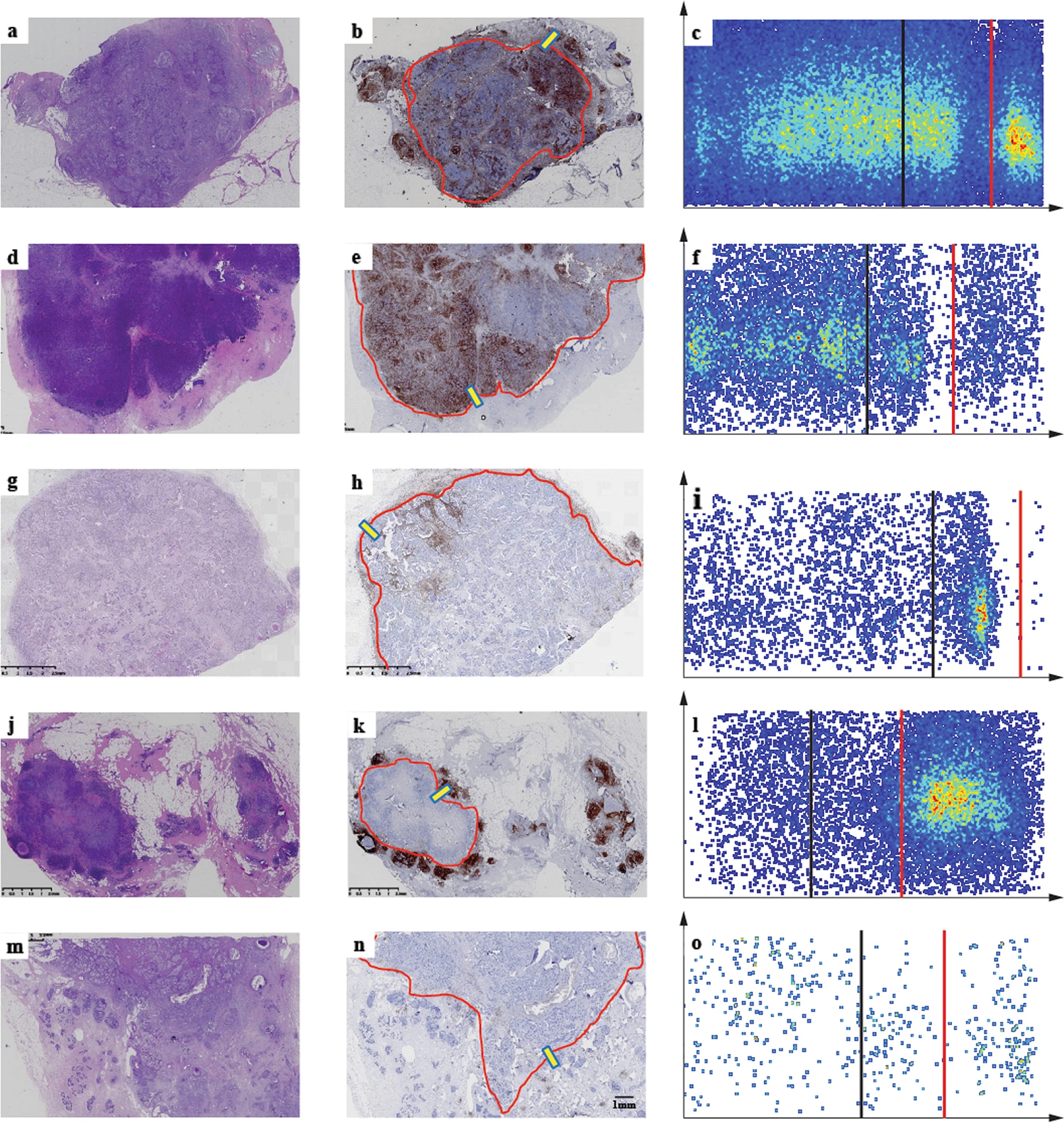
Figure 2 Distribution and morphology of immune cells in five IP patterns of breast cancer tissue.
H&E staining sections, IHC sections, and tissue cytology analysis results of IP1 (a-c), IP2 (d-f), IP3 (g-i), IP4 (j-l), and IP5 (m-o). Perform LCA labeling staining on IHC slices. The red line in the IHC slice indicates the edge of the tumor area. The organizational Gnostic analysis of the yellow frames in panels b, e, h, k, and n is shown in c, f, i, l, and o, respectively. The black and red lines displayed by Tissue Cytometry analysis represent the tumor area and the edge of the accessory tumor, respectively. H&E hematoxylin and eosin, IHC immunohistochemistry, IP immune mode, LCA leukocyte common antigen.
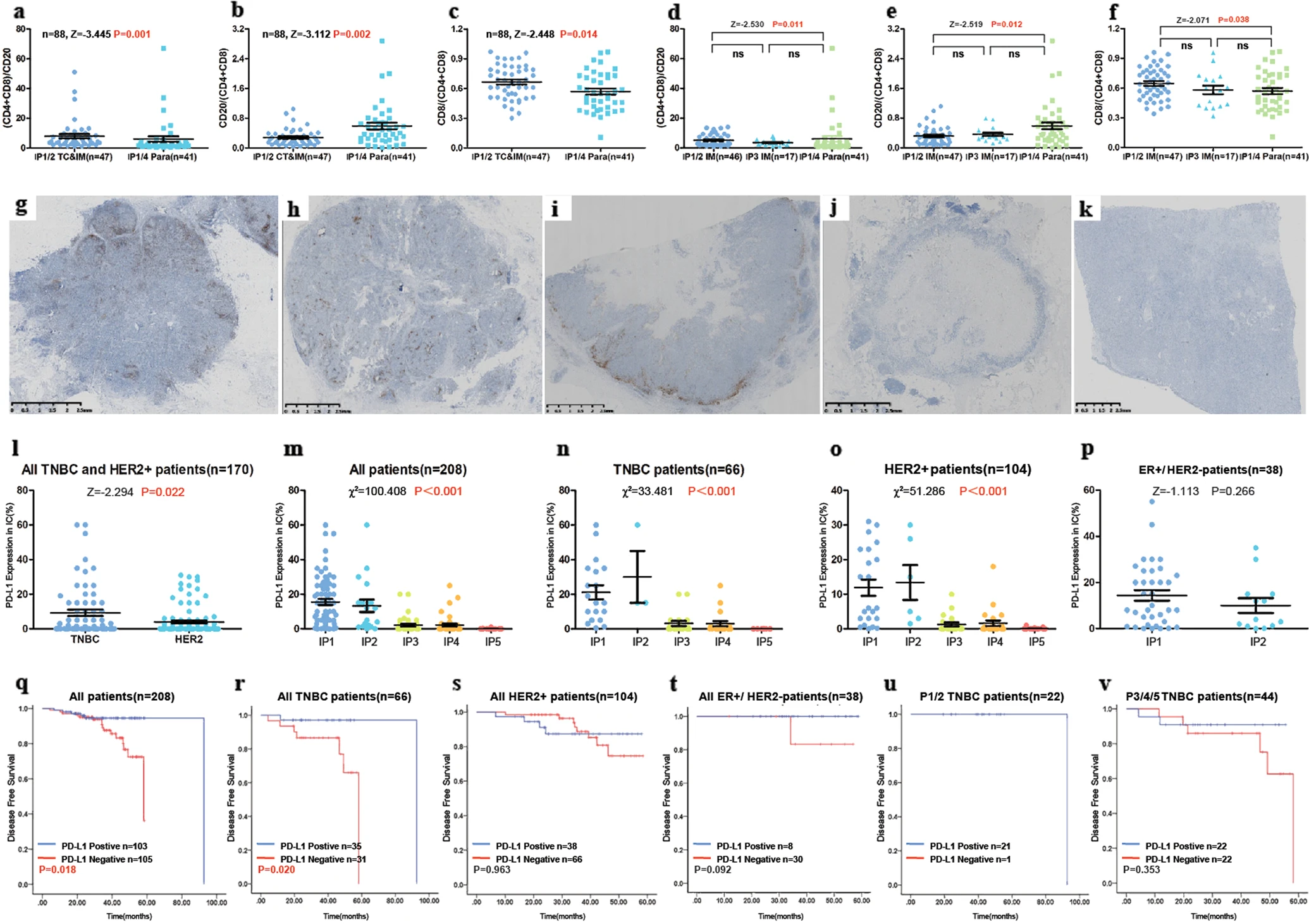
Figure 3 Different immune cell subpopulations were identified in the tumor associated and accessory tumor regions of all five IPs identified in this study.
In IP4/8 TC and IM, as well as IP20/20 Para, the ratio of T lymphocytes (CD4- and CD8 positive) to B lymphocytes (CD8 positive) a, B lymphocytes (CD1 positive) to T lymphocytes (CD2- and CD1 positive) b, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CD4 positive) to T lymphocytes c. The ratio of T lymphocytes to B lymphocytes d, B lymphocytes to T lymphocytes e, and cytotoxic T cells (CD4 positive) f to T lymphocytes in IP8/1 IM, IP2 IM, and IP3/1 Paras. PD-L1 positive immune cells (SP142, brown DAB staining) were observed in all five modes of g-k. The expression of PD-L1 in all five patterns is observed for all patients m, all TNBC or HER2+tumor patients, all TNBC n patients, all HER2+patients o, and all luminal HER2 − patients p. IP immune structure mode, TC tumor center, IM invasive margin, paraneoplastic region, TNBC triple negative breast cancer.
In recent years, AI tissue slicing analysis technology has been rapidly developing with the help of technology, but pathological interpretation of data still requires deep cooperation from pathological experts. The Tissue Cytometry technology, with its precise single-cell quantitative analysis capability and AI Classifier tissue recognition algorithm as its core, has achieved a data solution with the advantage of real image position analysis for the goal of in situ spatial distribution relationship analysis. Under this solution, the distribution relationship of all cells and tissues is calculated based on pixel distance, rather than evaluating vector distance as a spatial coordinate.
It is precisely because the Tissue Cytometry technology enables the analysis of the spatial distribution relationship between the structure and morphology of real tissue cells in slices, providing a solid and reliable data foundation, that the authors of the article were able to accurately interpret the data with solid and solid pathological interpretation standards and rich experience in pathological interpretation, and observed five immune structural patterns (IPs) significantly correlated with clinical pathological features, especially molecular subtypes, histological grading, clinical staging, and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression.
It is worth mentioning that, The article data is sourced from thousands of different stained sections of 579 patients, each of which was subjected to panoramic imaging and data analysis using Tissue Cytometry technology, both in terms of data reliability and research comprehensiveness, it has reached the international leading level.